Cashews are a rich, nutty, and buttery seed (yes seed, not nut) that is nutrient-dense and filled with healthy fats, protein, vitamins, and minerals! They are part of the family that includes mangoes, poison ivy, and pistachios, and are a quite unique food overall.
Although small in size, a simple serving of 1 ounce (28g) of raw cashews (about 18 cashews) is highly nutritious. According to the US Department of Agriculture database, these nuts contain the following per serving:
Nutritional Facts
Calories: 157
Carbs: 9g
Fat: 12g
- Saturated fat 2.2 g
- Polyunsaturated fat 2.2 g
- Monounsaturated fat 7 g
Protein: 5g
Fiber: 1g
Copper: 622mg (69% of Daily Values)
Iron: 1.9mg (10% of DV)
Magnesium: 83mg (21% of DV)
Manganese: 0.47 mg (20% of DV)
Zinc: 1.64 mg (15% of DV)
Phosphorus: 168mg (13% of DV)
Cashews also contain the following micronutrients: Selenium (10% DV), Thiamine (10% DV), Vitamin K (8% DV), Vitamin B6 (7% DV).
Where To Find Organic Cashews
This versatile superfood originates from cashew trees native to Brazil and is currently being cultivated worldwide, especially in Brazil, Vietnam, India, Nigeria, and Indonesia. The cashew actually grows outside the cashew apple, the accessory or false fruit of the tree, and are removed from the inedible shell.
The pale color of cashews results from removing the outer green shell and processing the nut rigorously through roasting and steaming to exterminate toxic oils for human consumption. These oils are made of the same ingredient found in poisonous ivy, urushiol, which is also found in the related mangoes and pistachios.
The cashew apples are also edible and can be eaten raw, cooked in curries, and even fermented into an alcoholic drink. It is also commonly used to make preserves, chutneys, and jams in countries the grow this unique fruits. The fruit has a light nutty sweet flavor and is also described as a slightly astringent taste and similar texture to a mango.
.jpg?width=1299&name=raw-cashews-apples-for-health-benefits%20(1).jpg)
After this extensive process, many experience the dilemma of either price or availability. Organic cashews can be out of the budget range or just not an option at your local market.
One company, Thrive Market, is well aware of this, so they offer excellent prices and a range of diet specific options and send them to your front door (ground-mail only, no air traffic)! Thrive, with their amazing values and mission, also provides a membership to a veteran or low-income family in need for each person that signs up! Check out some delicious products and prices to compare and see for yourself! Cashews can be found in stores raw, roasted, salted, and even in the form of nut butter, milk, and cheese!
- Raw Cashews
- Dry Roasted & Salted Cashews
- Organic Sriracha Cashews
- Cocoa Dusted Cashews
- Cashew Butter
- Cashew Cacao Spread
- Cashew Milk
- Cashew Cheesy Sauce
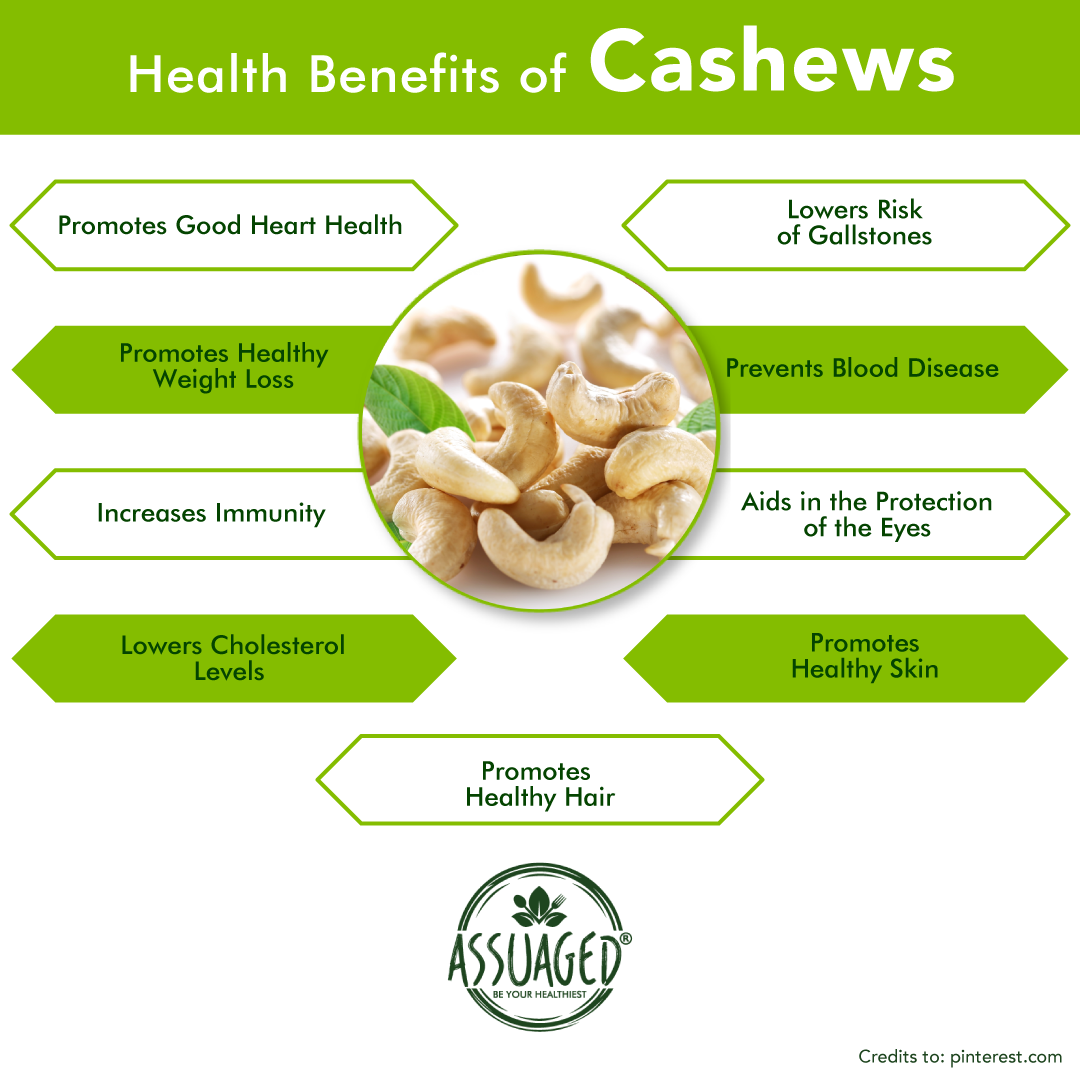
Benefits of Cashews on Heart Health
A handful of cashews provides a fair amount of protein, vitamins, and minerals, and are particularly rich in unsaturated fats, the healthy fats that your body needs! Replacing saturated fats with more unsaturated (monounsaturated and polyunsaturated) fats helps to reduce the risk of heart disease by improving the arteries’ conditions.
The term “fat” is loosely thrown around with a negative connotation. Dietary fats are more energy-dense than carbohydrates and proteins. Still, healthy fats provide energy, support cell growth, protect organs, and are required to uptake fat-soluble vitamins like Vitamins A, D, E, and K.
Types of Dietary Fats:
Saturated fats - are more solid at room temperature; this type typically comes from animal food sources. Frequent consumption can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke caused by the buildup of LDL (bad) cholesterol in the arteries.
Trans fats - are oils that undergo hydrogenation to achieve the consistency of saturated fats; this also increases LDL in the arteries and increases cardiovascular disease risk.
Unsaturated fats - are healthy fats that are often liquid at room temperature. These are monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, easily found in oils, nuts, and seeds. Moderate consumption helps with lowering the LDL and raising HDL (”good cholesterol”) in our blood vessels. This process decreases plaque buildup and the risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
The polyunsaturated fats, omega-3 and omega-6, are essential fatty acids in our diets. Our bodies cannot make these fats, so they must be obtained through our diets to support cell growth. These fats also play a role in blood clotting and inflammation.
The Power of a Cashew’s Micronutrient Content
Aside from its rich unsaturated fat content, the numerous vitamins and minerals also contribute to its powerful superfood title! Cashews are a good source of protein for their size! It is crucial to include sufficient amounts of protein to provide energy, build and repair muscles, and increase feelings of fullness.
Along with the dense energy quantity of macronutrients, cashews also have a diverse pool of micronutrient content; the function of these vitamins and minerals play a role in improving bone and joint health, immune function, and can help relax nerves.
Minerals
Copper - This mineral, which is high in cashews, is vital in maintaining healthy bones, blood vessels, making red blood cells, and supporting nerve and immune functions. Copper also plays a role in forming collagen and preventing osteoporosis.
Magnesium - Here’s an essential mineral that participates in over 300 enzyme reactions in the body. It also helps with muscle and nerve function, regulates blood pressure, and supports the immune system. Studies show that consuming sufficient Mg sources decreases Type 2 diabetes risk, which attributes to glucose control and insulin metabolism.
Manganese - Another essential trace mineral needed in small amounts to assist enzymes in processing amino acids, cholesterol, and glucose metabolism. The mineral is also associated with bone formation and blood clotting.
Zinc - This micronutrient plays a role in immune function and supports healthy growth and development during pregnancy, childhood, and adolescence. It is even required for a proper sense of taste and smell! Typically found in red meat and poultry, cashews and other nuts and legumes are excellent plant-based sources.
Phosphorus - A vital mineral found in this buttery nut is also a fundamental component of bones, teeth, DNA, and RNA. This mineral is a part of our cell membranes and makes up our body’s key energy source, ATP.
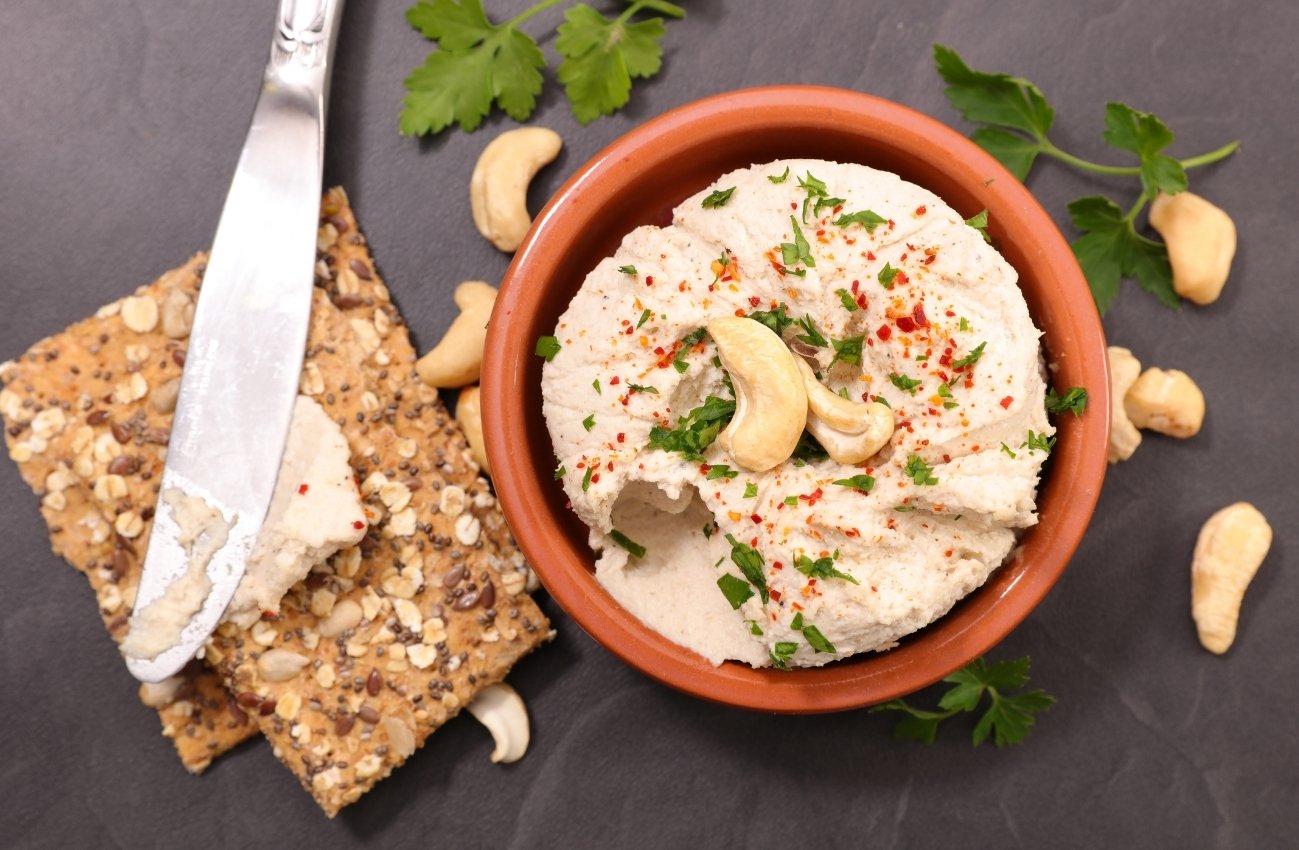

Want To Try Making Tasty Simple Recipes From Cashews?
Organic cashews can be enjoyed either raw or lightly roasted; the nutritional value is almost the same! By soaking them overnight, the range of uses in the kitchen expands to another level!
-
Easy Dairy-Free Sour Cream
-
Cashew Cream Cheese
-
Vegan Herb and Cheese Sauce
-
How To Make Cashew Milk
-
Homemade Vegan Ranch Dressing
-
Rainbow Champagne No-Bake Cheesecake
-
Vegan Alfredo Purple Pad Thai
-
Organic Vegan Eggnog for Digestive Health
Eating Too Many Cashews?
According to the American Heart Association, the recommendation is a small handful (1.5 ounces) of whole unsalted nuts or 2 ounces of nut butter a day for protein and fat intake!
Moderation is key, as going overboard has its own setbacks and health concerns. Healthy fats are good for your body, but a balance with carbs and proteins must be factored in for optimal health results.
Oxalate is present in our diets in low quantities and is usually excreted through urine. There is ample oxalate content in cashews, so over consumption combined with low calcium intake can eventually cause damage to the kidneys. It's important to remember the composition of cashews is a large portion of fats; so casual snacking can quickly result in a high-calorie intake and possibly weight gain.
So how are you going to start incorporating cashews into your diet? Let us know in the comments below! Do you have any recipes you’d like to share with the Assuaged community? If so, please check out our ➡️Share a Recipe⬅️ page!
Let us know if you have any other questions about this fantastic little superfood that packs a nutritious punch! Or if you'd like to learn more about getting protein and other nutrients on a plant-based diet, check out How To Get Complete Protein From A Plant-Based Diet!














.jpg)